Learn watch command to execute script or shell commands repeatedly every n seconds. Very much useful in automation or monitoring.

watch command is a small utility using which you can execute shell command or script repetitively and after every n seconds. Its helpful in automation or monitoring. Once can design automation by monitoring some code/command output using watch to trigger next course of action e.g. notification.
watch command is part of procps package. Its bundled with OS still you can verify if package is installed on the system. This utility can be used directly by issuing the watch command followed by command/script name to execute.
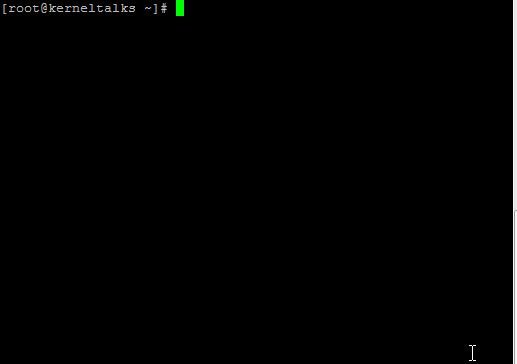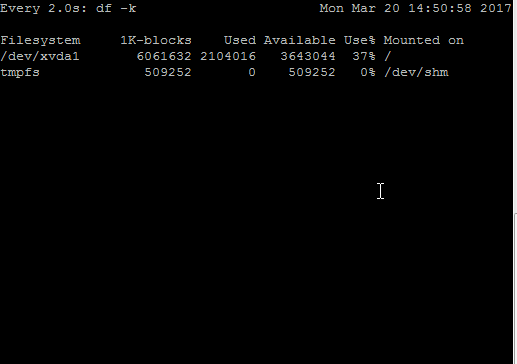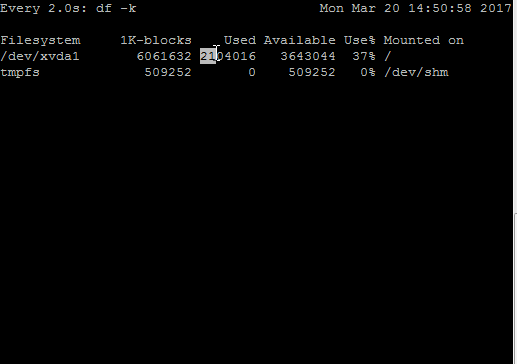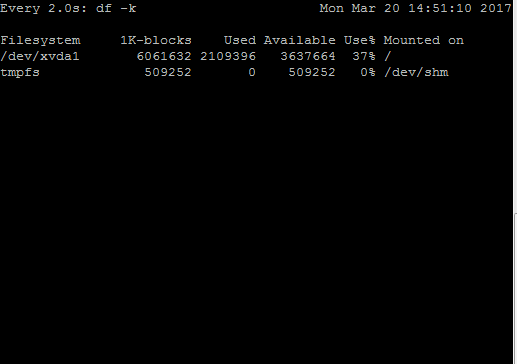
For example, I created a small script which writes junk data continuously in a file placed under /. This will change utilization numbers in df -k output. In the above GIF, you can see changes in the “Used” and “Available” column of df -k output when monitored with watch command.
In output, you can see –
- The default time interval is 2 seconds as shown n first line
- Time duration followed by a command which is being executed by watch
- The current date, time of server on the right-hand side
- Output of command being executed
Go through below watch command examples to understand how flexible the watch is.
Different options of watch
Now, to change the default time interval use option -n followed by time interval of your choice. To execute command after 20 seconds you can use :
# watch -n 20 df -k
Every 20.0s: df -k Mon Mar 20 15:00:47 2017
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/xvda1 6061632 2194812 3552248 39% /
tmpfs 509252 0 509252 0% /dev/shm
See above output, interval is changed to 20 seconds (highlighted row)
If you want to hide header in output i.e. time interval, the command being executed, and current server date, time, use -t option. It will strip off the first line of output.
# watch -t df -h
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/xvda1 6061632 2194812 3552248 39% /
tmpfs 509252 0 509252 0% /dev/shm
Highlighting difference in the present and previous output is made easy with -d option. To understand this, watch below GIF –
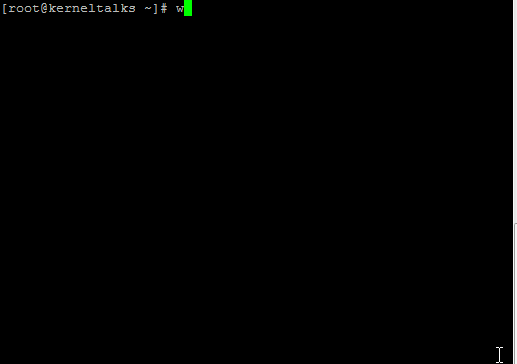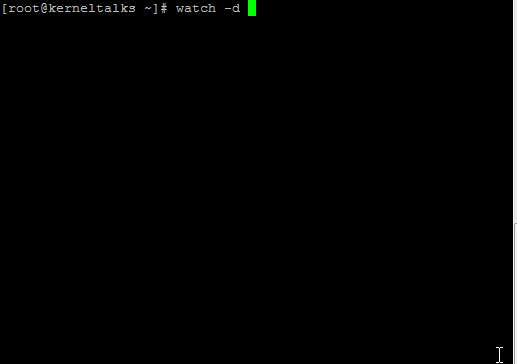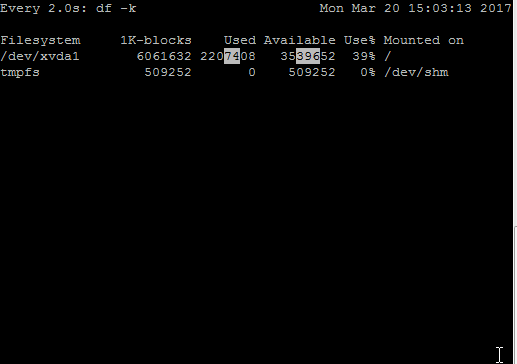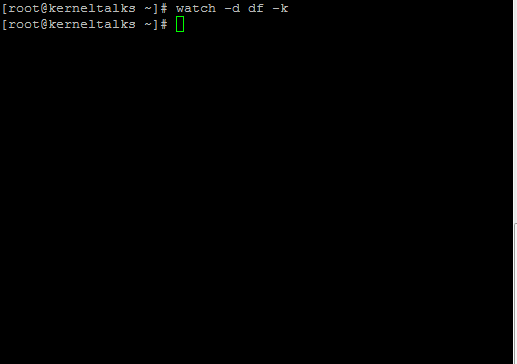
In the above output, I used the same data writing script to fill /. You can observe the only portion which is different from the previous output is being highlighted by watch in the white box!
Share Your Comments & Feedback: