Quick article to demonstrate how to configure port forwarding in Linux using iptables.
In this article, we will walk you through port forwarding using iptables in Linux. First of all, you need to check if port forwarding is enabled or not on your server. For better understanding, we will be using eth0 as a reference interface and all our command executions will be related to eth0 in this article.
How to check if port forwarding is enabled in Linux
Either you can use sysctl to check if forwarding is enabled or not. Use below command to check –
[root@kerneltalks ~]# sysctl -a |grep -i eth0.forwarding
net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding = 0
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.forwarding = 0
Since both values are zero, port forwarding is disabled for ipv4 and ipv6 on interface eth0.
Or you can use the process filesystem to check if port forwarding is enabled or not.
[root@kerneltalks ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/eth0/forwarding
0
[root@kerneltalks ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/eth0/forwarding
0
Again here process FS with zero values confirms port forwarding is disabled on our system. Now we need to first enable port forwarding on our system then we will configure port forwarding rules in iptables.
How to enable port forwarding in Linux
As we checked above, using the same methods you can enable port forwarding in Linux. But its recommended using sysctl command rather than replacing 0 by 1 in proc files.
Enable port forwarding in Linux using sysctl command –
[root@kerneltalks ~]# sysctl net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding=1
net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1
[root@kerneltalks ~]# sysctl net.ipv6.conf.eth0.forwarding=1
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1
To make it persistent over reboots, add parameters in /etc/sysctl.conf
[root@kerneltalks ~]# echo "net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1">>/etc/sysctl.conf
[root@kerneltalks ~]# echo "net.ipv6.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1">>/etc/sysctl.conf
[root@kerneltalks ~]# sysctl -p
net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1
Now, we have port forwarding enabled on our server, we can go ahead with configuring port forwarding rules using iptables.
How to forward port in Linux
Here we will forward port 80 to port 8080 on 172.31.40.29. Do not get confused port forwarding with port redirection.
We need to insert an entry in PREROUTING chain of iptables with DNAT target. Command will be as follows –
# iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to 172.31.40.29:8080
# iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -d 172.31.40.29 --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
Change interface, IP and ports as per your requirement. The first command tells us to redirect packets coming to port 80 to IP 172.31.40.29 on port 8080. Now packet also needs to go through FORWARD chain so we are allowing in in the second command.
Now rules have been applied. You need to verify them.
How to check port forwarding iptables rules
Command to verify port forwarding rules is –
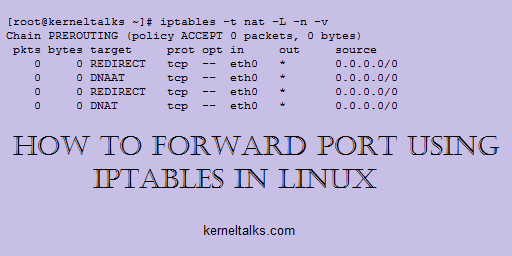
[root@kerneltalks ~]# iptables -t nat -L -n -v
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DNAT tcp -- eth0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 to:172.31.40.29:8080
Here REDIRECT target means its a redirection rule. Since we have configured forwarding rule we see the target as DNAT
How to save iptables rules
To save iptables rules and make them persistent over reboots use below command –
[root@kerneltalks ~]# iptables-save
Maybe an update/addition using nftables regarding this subject?.
you should add possibility to test your forwarding with kind of curl/wget calls.
so the guide will be complete. In this way which it represented it is just a theory…