Learn how to restart inetd service in Linux. Xinetd service is a replacement for inetd service in new Linux versions.
inetd is internet daemon. Inetd is responsible for internet services like telnet, pop3, ftp, etc. Whenever a packet comes over the network to a server on a particular port, inetd is responsible to check it and launch the appropriate program to handle the connection request. For checking port information and its related services it consults /etc/services file.
Below is a list of commands to manage inetd service. In newer systems inetd is replaced with more powerful daemon xinetd.
Start inetd service
# /etc/init.d/inetd start
Stop inetd service
# /etc/init.d/inetd stop
Restart inetd service
# /etc/init.d/inetd restart OR # killall -HUP inetd
All inetd configuration can be found in file /etc/inetd.conf
On newer systems, inetd is being replaced by xinetd. xinetd is an Extended internet daemon. If you fail to run above command your system probably runs xinetd as an inetd replacement. In that case, follow below commands –
Start inetd service
# service xinetd start
Stop inetd service
# service xinetd stop
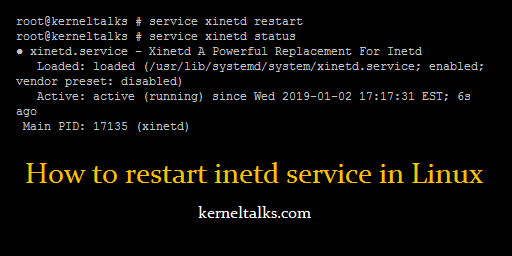
Restart inetd service
# service xinetd restart
Check xinetd service state
root@kerneltalks # service xinetd status
● xinetd.service - Xinetd A Powerful Replacement For Inetd
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/xinetd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2019-01-02 17:17:31 EST; 6s ago
Main PID: 17135 (xinetd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 512)
CGroup: /system.slice/xinetd.service
└─17135 /usr/sbin/xinetd -stayalive -dontfork
All the services being handled by xinetd can be found under/etc/xinetd.d directory. Each service has its own configuration file under /etc/xinetd.d directory.
Linux is huge and complicated. Please indicate date, distro, os version, desktop when posting!