A how-to guide for the installation of patch or software on the HPUX operating environment. This includes steps to install, configure, and verify.

This post is a how-to guide that has steps to install, configure, and verify patch or software on HPUX operating system. Before we begin the patching process, one needs to finalize the downtime window for patching with the concerned team. Also, if individual patches are planned to install then patch ID needs to be known to download from the HP portal. HP Passport ID required to sign-in on the HP portal.
Also read: HPUX patch naming conventions
HPUX patching enables a system with new features, enhancements and removes bugs if any. HP releases patch bundles for HPUX every 6 months i.e twice in a year. These bundles can be downloaded and applied to the system. Also, individual patches can be downloaded. For individual patches, one should know the patch ID first.
Prerequisite :
- Log in to the HP portal and download required patches. HP provides the facility to download your required patch along with its all dependencies so you need not to again search for dependencies separately. When prompted for download, select the gzip bundle format.
- Upload the patch on the server using FTP. Unzip patch file which will have
create_depotscript inside. When executed, this script will create$PWD/depotdirectory which includes all patches to be installed. Make sure depot is created properly using:
# /usr/sbin/swlist -s /tmp/PACPTHP_00001.depot
# Initializing...
# Contacting target "testsrv2"...
#
# Target: testsrv2:/tmp/PACPTHP_00001.depot
#
#
# No Bundle(s) on testsrv2:/tmp/PACPTHP_00001.depot
# Product(s):
#
HPOvLcore 6.00.000 HP Software Core Functionality
HPOvLcore 6.00.000 HP Software Core Functionality
HPOvPerf 4.70.000 HP OpenView Performance
HPOvPerf 4.70.000 HP OpenView Performance
- A server backup is an important thing to be done before any activity. Take ignite backup over network or tape. Also collect nickel, sysinfo outputs from the server. Ensure the downtime window and other related ITIL processes are completed and approved.
Installation & configuration :
Before starting activity make sure all applications on the server are brought down by respective parties. Once confirmed, proceed with patch installation. Install the patch using the command:
# /usr/sbin/swinstall -s /tmp/PACPTHP_00001.depot
NOTE: The interactive UI was invoked, since no software was
specified.
Starting the terminal version of swinstall...
To move around in swinstall:
- use the "Tab" key to move between screen elements
- use the arrow keys to move within screen elements
- use "Ctrl-F" for context-sensitive help anywhere in swinstall
On screens with a menubar at the top like this:
------------------------------------------------------
|File View Options Actions Help|
| ---- ---- ------- ------------------------------- ---|
- use "Tab" to move from the list to the menubar
- use the arrow keys to move around
- use "Return" to pull down a menu or select a menu item
- use "Tab" to move from the menubar to the list without selecting a menu item
- use the spacebar to select an item in the list
On any screen, press "CTRL-K" for more information on how to use the keyboard.
This will start the text-based GUI. You can navigate in this GUI menu using, arrow keys and SPACE key. Select the all listed patches using arrow key and space bar to highlight them.
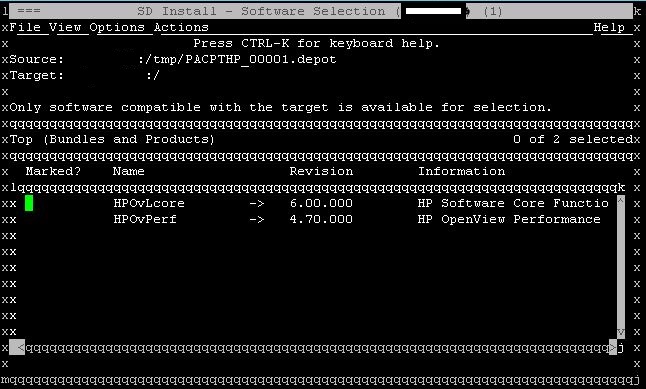
Once marked, select Install option from the Actions menu.
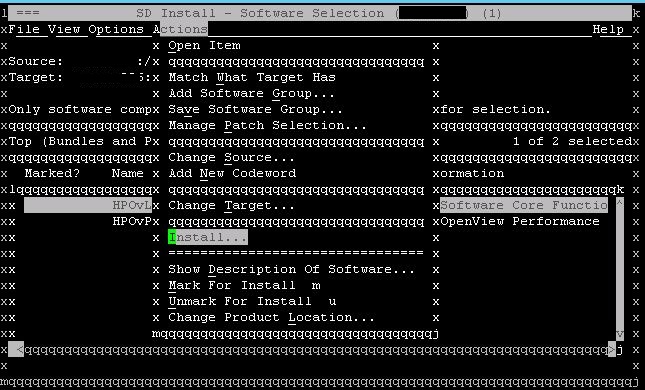
This will take time to install and configure the patch in the system depending upon the size of the depot. This configuration happens in the background with this command execution only.
If the required system will be rebooted post-installation. To check if the patch needs a reboot after install, you can run above swinstall command with -p preview option. Which will just check dependencies, depot health, and show you report. This report includes if a reboot is required or not. Even while downloading the patch from the HP portal, you can view its details which also includes information about reboot requirements.
Verification :
Once the installation is complete, or after reboot, check if all installed patches are configured in the kernel or not using the command :
# swlist -l fileset -a state | grep –v –e “#” –e “configured”
The output of the above command should be blank. If there are any file sets left in an unconfigured/installed state then the above command’s output will reveal it. So, if the output is not blank, you need to configure these unconfigured/installed state file sets manually. To configure all patches again use below command:
# /usr/sbin/swconfig \ *
======= 12/27/16 10:17:15 SST BEGIN swconfig SESSION
(non-interactive) (jobid=testsrv2-0396)
* Session started for user "root@testsrv2".
* Beginning Selection
* Target connection succeeded for "testsrv2:/".
----- output clipped -----
* Selection succeeded.
* Beginning Analysis
* Session selections have been saved in the file
"/home/user3/.sw/sessions/swconfig.last".
* "testsrv2:/": 2831 filesets have already been configured.
* Analysis succeeded.
* Beginning Execution
* "testsrv2:/": 2831 software objects were determined to be
skipped in the analysis phase.
* Execution succeeded.
NOTE: More information may be found in the agent logfile using the
command "swjob -a log testsrv2-0396 @ testsrv2:/".
======= 12/27/16 10:17:59 SST END swconfig SESSION (non-interactive)
(jobid=testsrv2-0396)
This command will try to configure the remaining patches. After completion of this command, once again verify your installation.
Share Your Comments & Feedback: